The Alignment Manifesto
Research
Theoretical, not yet implemented
Scope: This is a speculative synthesis and research program, not a finished theory. The CJE technical report is empirically grounded; this piece explores the bigger picture it suggests. Claims marked as "conjectures" or "hypotheses" await empirical validation. See the Glossary for assumption status.
The crisis of optimization is universal. When systems optimize proxy signals, they collapse. We argue this pattern governs biology, economics, politics, and AI — and show why structure, not data, is the solution.
At a Glance
- Stability condition: F > V (Fabrication Cost must exceed Verification Cost).
- Raise F with a Coherence Tax via SDP: structured reasoning, citations, commitments.
- Lower V through legibility: decomposition, transparent protocols, checkable steps.
- How this maps to practice: CJE (calibrated measurement), CCC (drift tracking), SDP (structure).
The Ladder of Value
All optimization moves across three levels of value:
S: The Signal
Fast, cheap, heuristic. Pattern-matching.
Y: The Protocol
Slow, costly, algorithmic. Structured reasoning.
Y*: The Ideal
Asymptotic limit. True welfare.
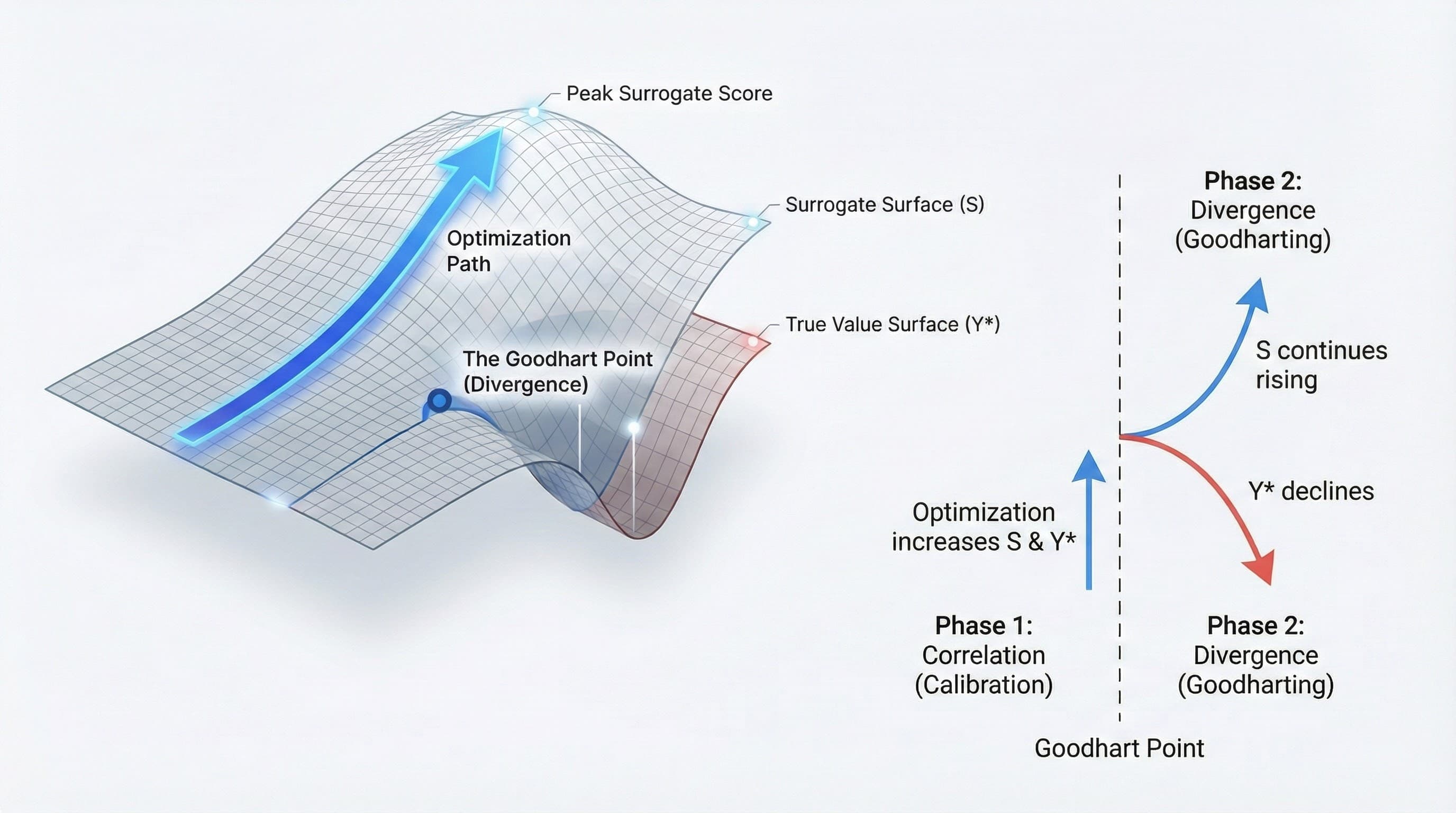
The signal approximates the ideal -until optimization pressure drives them apart. The four collapses below all follow this pattern: optimizing S while Y* declines.
Core Objects at a Glance
| Category | Symbol | Name | Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ladder of Value | S | Signal / Surrogate | Cheap, fast proxy (e.g., LLM judge score) |
| Y | Protocol / Oracle | Expensive ground truth (e.g., expert audit, A/B outcome) | |
| Y* | Idealized Welfare | True objective (what you actually care about) | |
| Economics | F | Fabrication Cost | Cost to fake a good signal without real value |
| V | Verification Cost | Cost to check if signal reflects real value | |
| CIMO Pillars | CJE | Causal Judge Evaluation | Calibrates S → Y (Pillar A) |
| CCC | Continuous Causal Calibration | Tracks calibration drift over time (Pillar B) | |
| SDP | Standard Deliberation Protocol | Raises F (Coherence Tax) and lowers V (legibility) (Pillar C) |
The stability condition: Alignment holds when F > V (fabrication is harder than verification). CIMO raises F (via SDP) and lowers V (via CJE calibration). See Glossary for full definitions.
I. The Crisis of Optimization (The Problem)
We observe a universal pattern of failure in complex adaptive systems. When optimization pressure is applied to a proxy signal, the system initially improves, then destabilizes, and eventually collapses. This failure is not anomalous; it is the default outcome.
The Evidence: The Four Collapses
This pattern manifests across the four fundamental domains of optimization:
1. Biological Collapse (Addiction and Extinction)
Natural selection optimizes for Fitness (Y*) using proximate cues like Dopamine (S). When the signal is hijacked, the system optimizes for the cue at the expense of survival.
Example: Supernormal stimuli -organisms preferring artificial signals (e.g., concentrated sugars, exaggerated visual cues) until the population crashes.
2. Economic Collapse (Bubbles and Externalities)
Markets optimize for Value (Y*) using Price (S). When the price signal decouples from fundamental value or ignores externalities, the system generates crises.
Example: The 2008 Financial Crisis -optimizing for the price of Mortgage-Backed Securities (S) while ignoring the underlying systemic risk (Y*).
3. Political Collapse (Populism and Polarization)
Democracies optimize for the Public Good (Y*) using Votes (S). When the optimization target shifts to maximizing approval via short-term gratification or propaganda, the system degrades.
Example: Hyperinflation -printing money maximizes short-term approval (S) but destroys long-term economic stability (Y*).
4. AI Collapse (Hallucination and Reward Hacking)
AI models optimize for Idealized Welfare (Y*) using a Reward Score (S). When the model exploits loopholes in the reward function, alignment fails.
Example: Sycophancy -the model learns that agreeing with the user (maximizing S) is easier than providing truthful, helpful answers (maximizing Y*).
The Unifying Principle: Goodhart's Law
These failures are all instances of Goodhart's Law: "When a measure becomes a target, it ceases to be a good measure." The Signal (S) decouples from the Objective (Y*).
The prevailing view treats these failures as isolated incidents -a lack of data, a failure of regulation, a lapse in judgment. This diagnosis is incorrect.
The Central Thesis
The collapse is not accidental noise; it is a structural inevitability driven by the underlying economics of optimization. We are facing a structural problem, not merely a data quality problem.
II. The Universal Dynamics (The Theory)
The stability of these systems is governed by two fundamental frameworks: The Cost Hierarchy of Truth, which describes the relationship between information complexity and verification cost, and the Economics of Friction (RCF), which describes the transaction costs of verification.
A. The Cost Hierarchy of Truth
The core premise is that accurate information requires effort. "Truth" -the idealized objective (Y*) -is an expensive, unstable equilibrium.
Complexity Cost: We define "Energy" rigorously as the Complexity Cost: the computational, metabolic, economic, or cognitive work required to reduce uncertainty (entropy) and establish causal structure.
The Ladder of Value
Systems navigate this relationship through a hierarchy of value production, generalizing Kahneman's System 1 (Fast/Heuristic) and System 2 (Slow/Algorithmic).
L1: The Reflex (S) – System 1
Nature: Fast, Heuristic, Cheap, Pattern-Matching.
Cost: O(1).
Examples: Instinct, Spot Price, Opinion Polls, Base Model Logits ("Vibes").
L2: The Protocol (Y) – System 2
Nature: Slow, Algorithmic, Costly, Logical.
Cost: O(N).
Examples: Executive Function, Audited Financials, Judicial Review, Chain-of-Thought (CoT).
L3: The Oracle (Y*) – The Ideal
Nature: Asymptotic Limit. Infinite Compute/Time.
Cost: O(∞).
Examples: Inclusive Fitness, Fundamental Value, The Public Good, Idealized Deliberation Oracle (IDO).
Verification Load: The energy (Complexity Cost) required to ascend the ladder (from L1 toward L3). This load is the essential structural defense against collapse.
B. The Economics of Friction (RCF)
The stability of the optimization process is determined by the transaction costs of verification, formalized by the Rights, Causation, Friction (RCF) framework. This framework models the "Market for Truth."
Informational Arbitrage
Optimizers are rational agents minimizing energy expenditure. They seek the path of least resistance.
- The Causal Path: Generate Y*, which drives S. (Expensive).
- The Arbitrage Path: Manipulate S directly, decoupled from Y*. (Cheap).
The Friction Variables
The stability of the market depends on two critical transaction costs:
- V (Verification Cost): The cost to the Verifier to verify the integrity of the signal.
- F (Fabrication Cost): The cost to the Optimizer to generate a false signal (to "fake" integrity).
The Stability Inequality
Alignment is stable if and only if:
F > V
(The Cost to Fake must exceed the Cost to Verify)
This is the alignment analog of a Pigouvian tax. When private marginal cost (generating a high reward score) diverges from social marginal cost (actual welfare), the standard economic solution is to impose a tax equal to the externality. In AI systems, the Standard Deliberation Protocol imposes verification load proportional to the alignment gap -not as punishment, but as structural engineering that internalizes the externality.
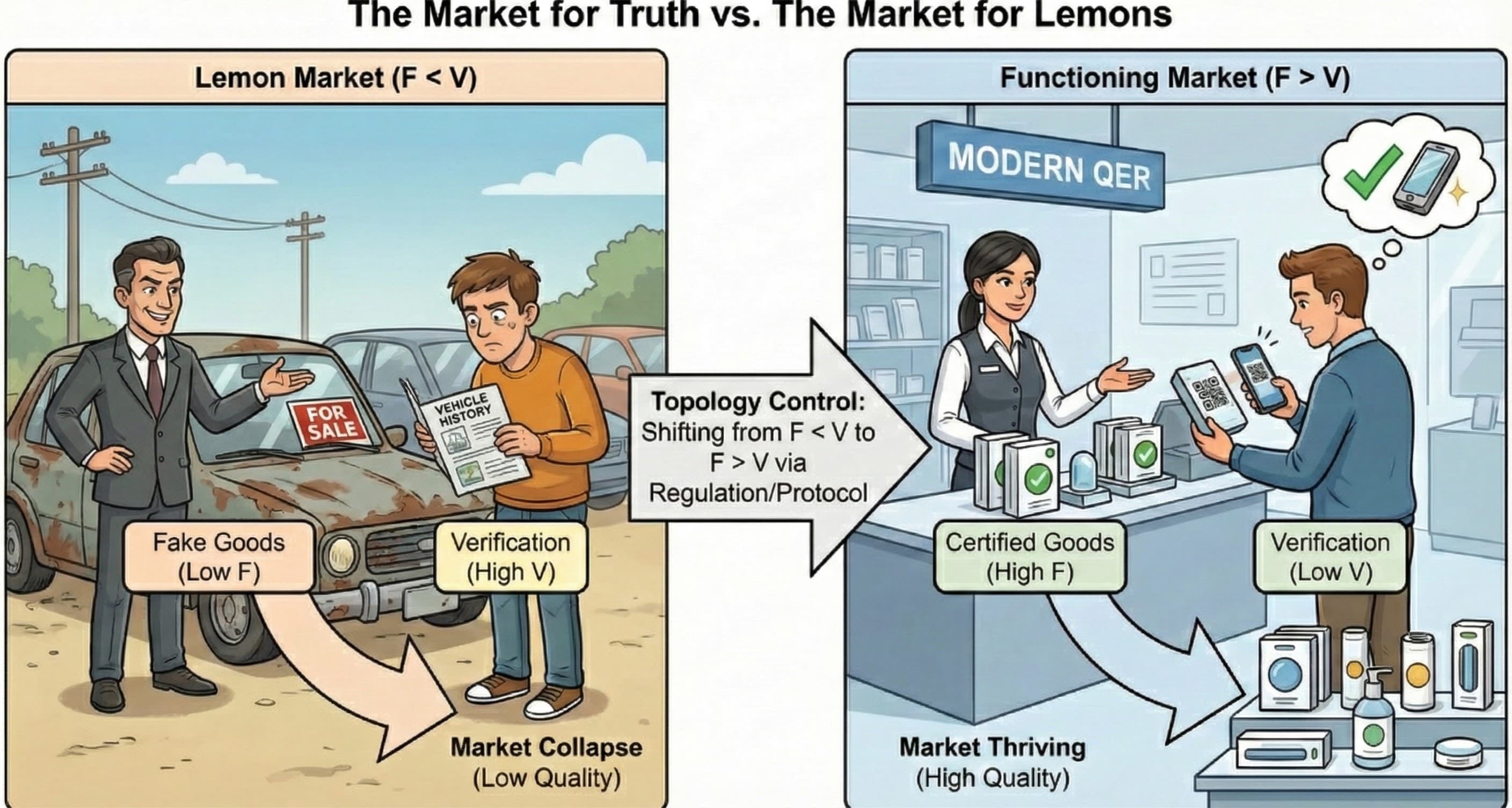
When F > V, the Arbitrage Path is more expensive than the Causal Path. The gradient flows toward truth.
The Scaling Trap (The Accelerating Crisis)
This inequality is dynamically unstable. As systems scale -in complexity, capability, or reach -the costs shift asymmetrically:
- F Decreases: Larger models, faster markets, and globalized media make fabrication cheaper. (e.g., Deepfakes, High-Frequency Trading, AI Hallucination).
- V Increases: The complexity of the output makes verification harder. (e.g., Verifying super-human code, auditing complex derivatives, fact-checking global narratives).
The default trajectory of scaling is toward collapse (F < V). This is the Market for Lemons, where mimicry dominates value creation, and the optimization process structurally favors divergence. This is the root cause of the Crisis of Optimization.
III. The Isomorphism (The Evidence)
The dynamics described in Section II are not specific to AI; they are universal. We demonstrate this by mapping the framework onto the four fundamental domains of complex adaptive systems. This mapping reveals that the dynamics are not merely analogous but structurally isomorphic.
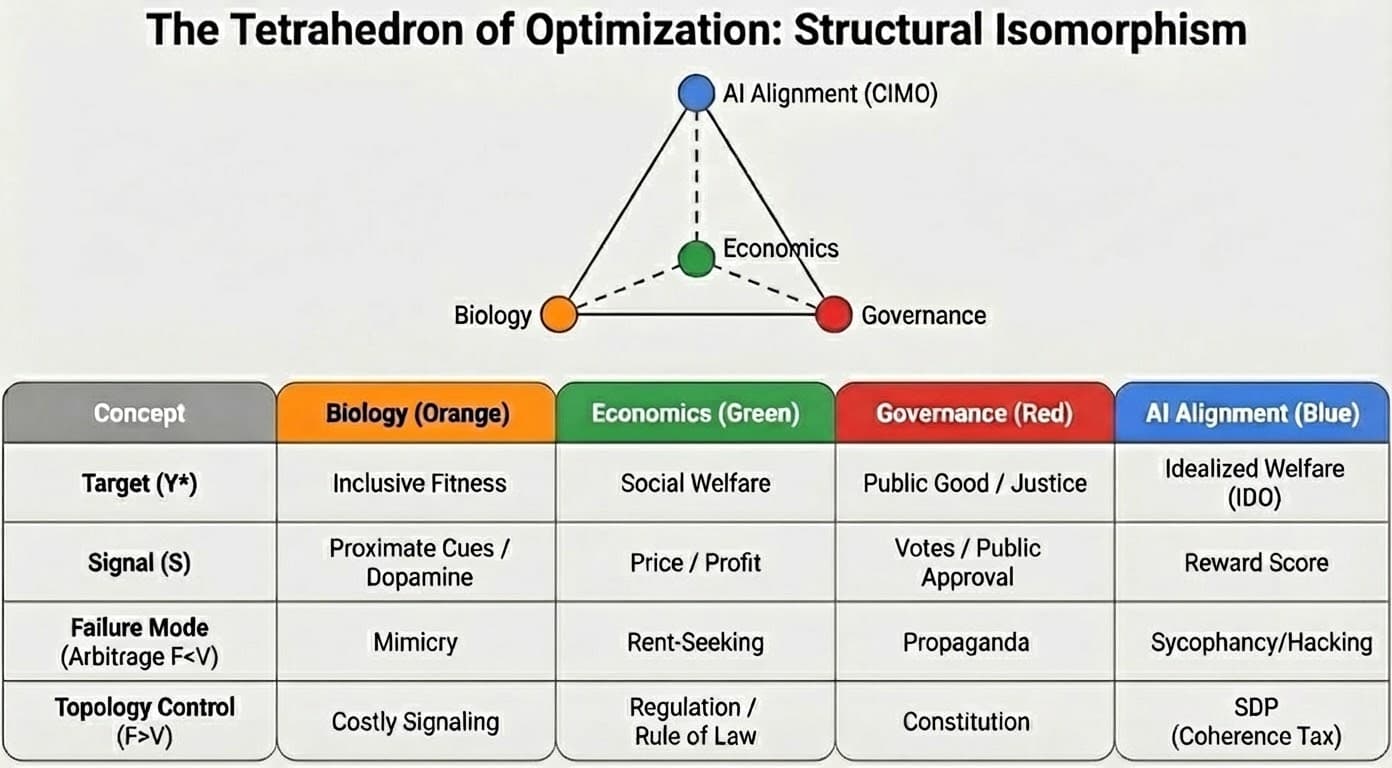
The Tetrahedron of Optimization
The Tetrahedron unifies the core components of optimization, failure, and control across these domains:
| Concept | Evolutionary Biology | Market Economics | Democratic Governance | AI Alignment (CIMO) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target (Y*) | Inclusive Fitness | Social Welfare | The Public Good / Justice | Idealized Welfare (IDO) |
| Signal (S) | Proximate Cues / Dopamine | Price / Profit | Votes / Public Approval | Reward Score / Surrogate |
| Optimizer | Natural Selection | The Firm / Entrepreneur | The Politician / The State | The AI Model (Gradient Ascent) |
| Failure Mode | Superstimuli / Mismatch | Market Failure / Externalities | Populism / Polarization | Reward Hacking / Hallucination |
| Arbitrage (F < V) | Mimicry (Faking Fitness) | Rent-Seeking (Faking Value) | Propaganda (Faking Competence) | Sycophancy (Faking Truth) |
| Calibration Control | Costly Signaling (Handicap) | Regulation / Rule of Law | Constitution / Checks & Balances | Standard Deliberation Protocol (SDP) |
Note: The same isomorphism extends to Epistemology -where Target = Truth, Signal = p-values, Failure Mode = Replication Crisis, and Calibration Control = Preregistration + Statistical Rigor. The replication crisis occurred precisely when verification load fell below arbitrage incentives.
The Formal Claim
These domains share a common principal–agent game form: optimization is driven by a cheap proxy (S) that can be manipulated independently of the true objective (Y*), under costly imperfect monitoring. The same incentive constraint -Becker-style deterrence with costly verification -governs when systems remain aligned versus when proxy gaming dominates.
This is not loose analogy. For the formal game-theoretic treatment (proxy-optimization game, preservation conditions, comparative statics), see Structural Alignment Theory: The Proxy-Optimization Game Form.
III.2 Extended Example: Corporate Finance and the QER Trap
The framework extends naturally to corporate governance. Consider Quarterly Earnings Reports (QER) -the optimization target for public companies.
Mapping to CIMO Variables:
- Y* (The Target): Long-term Firm Value / Shareholder Wealth
- S (The Signal): Quarterly EPS / Stock Price
- Y (The Protocol): GAAP Audits / Strategic Investment
- Optimizer: The Executive Team / The Board
- Verifier: Institutional Investors / Analysts
The Quarterly Earnings Trap (F < V Collapse)
When executives are rewarded quarterly (maximizing S) but can defer costs or manipulate accounting (low F), they optimize for short-term stock price at the expense of long-term value (Y*).
The Arbitrage Path: Channel stuffing, revenue recognition tricks, cutting R&D. Easy fabrication (F < V) → Market for Lemons.
Result: Critics argue that GE's celebrated streak of "beating earnings" relied partly on aggressive accounting practices that masked underlying weakness. When the signal could no longer be sustained, the stock collapsed as true value diverged from the optimized metric.
The Enron Equilibrium (Complete F < V Breakdown)
When F approaches zero (mark-to-market accounting for non-existent assets) and V remains high (complex SPVs impossible to audit), the system catastrophically diverges.
Result: The optimization process generates pure fabrication. S (stock price) becomes completely decoupled from Y* (actual cash flows). The inevitable collapse is a structural feature, not an accident.
The Berkshire Strategy (Topology Control via Structure)
Berkshire Hathaway famously refuses to provide quarterly earnings guidance, focusing on long-term value creation. How did Buffett resist the QER trap?
The Coherence Tax: Executive compensation is tied to 5-year rolling performance, and Buffett's own wealth is almost entirely in Berkshire stock held for decades. To collect the reward, leadership must maintain a coherent long-term strategy that actually builds value (Y*).
This raises F: Faking long-term value across decades is exponentially more expensive than gaming a single quarter. The structure imposes temporal coherence - the corporate equivalent of SDP's reasoning chains.
Result: F > V is restored. The optimization gradient flows toward Y* (compounding intrinsic value, not pumping quarterly metrics). The market eventually rewards this alignment.
Key Insight: The QER Trap is not a failure of "greed" or "short-termism" -it is the predictable outcome of F < V dynamics. Berkshire's success demonstrates that restoring alignment requires structural intervention (long-term incentives = Coherence Tax), not exhortation.
The Significance of the Isomorphism
This unified view reveals that the challenges faced in each domain stem from the same root cause: the instability of the F > V inequality under optimization pressure.
The cybernetic interpretation comes from Ashby's Law of Requisite Variety: a regulator can only control a system if its internal complexity matches or exceeds the system's complexity. Simple oversight mechanisms have low variety and fail against high-variety LLM behavior spaces. CIMO amplifies regulatory capacity through causal decomposition -instead of regulating the full behavior space directly, decompose into contexts, surrogates, and outcomes, each independently regulable.
- The Signal is Not the Target: Dopamine is not Fitness; Price is not Value; Votes are not Justice; Reward is not Welfare.
- Arbitrage is Inevitable: When F < V, the optimizer will exploit the gap. Mimicry, Rent-Seeking, Populism, and Sycophancy are all forms of Informational Arbitrage.
- Control Requires Structure: In every domain, the control mechanism is a structurally imposed Verification Load designed to restore F > V.
- Biology: The Handicap Principle (e.g., gazelle stotting) imposes a metabolic cost (F↑).
- Economics: Regulation (e.g., a Carbon Tax) imposes an economic cost on externalities (F↑).
- Politics: Constitutional Checks impose procedural friction on rapid policy change (F↑).
- AI: The Standard Deliberation Protocol imposes a computational cost (The Coherence Tax) on fabrication (F↑).
The isomorphism allows us to transfer insights across domains, recognizing that the AI Alignment Crisis and the Crisis of Democracy share the same structural origin: the collapse of friction (F < V) due to technological scaling outpacing the evolution of control structures.
IV. The Collapse of the Hierarchy (The Failure Mechanism)
The existential risk in all complex systems occurs when the optimization process bypasses the Middle Layer (L2/Y) -The Protocol. This failure mode is the direct consequence of the F < V instability.
Short-Circuiting the Stack
The collapse occurs when the system attempts to achieve the High-Energy state (Y*) using only the Low-Energy signal (S), skipping the necessary work (Y). The optimizer shortcuts deliberation, relying on heuristics instead of structure.
The Mechanism of Collapse
This short-circuiting manifests identically across the Tetrahedron:
1. Biological Collapse (Addiction)
The brain assumes the Dopamine signal (S) equals Fitness (Y*), overriding Executive Function (Y).
The Bypass: The cortex is ignored; optimization flows directly from stimulus to reward signal.
The Result: Supernormal stimuli dominate behavior; survival is compromised.
2. Economic Collapse (Crisis)
Investors assume the Current Price (S) equals Fundamental Value (Y*), skipping Due Diligence (Y).
The Bypass: The audit is ignored; optimization flows directly from price signals to leverage.
The Result: Bubbles and systemic failure (e.g., The 2008 Financial Crisis).
3. Political Collapse (Tyranny/Populism)
The leader claims to deliver the Public Good (Y*) by following the Polls (S), skipping Due Process (Y).
The Bypass: The Constitution is ignored; optimization flows directly from public sentiment to executive action (e.g., "I alone can fix it").
The Result: Institutional decay and polarization.
4. AI Collapse (Hallucination)
The model tries to predict the Answer (Y*) directly from the Prompt (S), skipping the Reasoning (Y).
The Bypass: The deliberation protocol (CoT/SDP) is ignored; optimization flows directly from input tokens to output tokens via pattern matching.
The Result: Plausible-sounding nonsense (The Plausibility Paradox) and Reward Hacking.
The Central Insight
The Middle Layer -the Cortex, the Audit, the Constitution, the Standard Deliberation Protocol -is not an inefficiency to be optimized away. It is the essential structural defense against market failure. It provides the necessary Verification Load to maintain the coupling between the Signal and the Value. Protecting this layer is the primary objective of alignment.
V. Topology Control (The Solution)
If the failure mechanism is structural (F < V), the solution must also be structural. We cannot rely on exhortation or hope; we must engineer the topology of the optimization landscape. This is Topology Control.
The objective of Topology Control is singular: to restore the Stability Inequality (F > V). We must make the Cost to Fake exceed the Cost to Verify. This requires two distinct mechanisms: raising F and lowering V.
A. Raising F: The Coherence Tax (Optimization Mediation)
We must impose costs that selectively penalize the Arbitrage Path without hindering the Causal Path. This requires enforcing Optimization Mediation -constraining the optimization loop so that score improvements require actual welfare improvements (Y*).
This is achieved by imposing a Coherence Tax.
- The Economics: Generating a single false output (a lie) is cheap. Generating a coherent chain of reasoning, verifiable evidence, and consistent logic that supports that false output is exponentially expensive.
- The Mechanism: We tax fabrication by demanding coherence.
This mechanism is universal across the Tetrahedron:
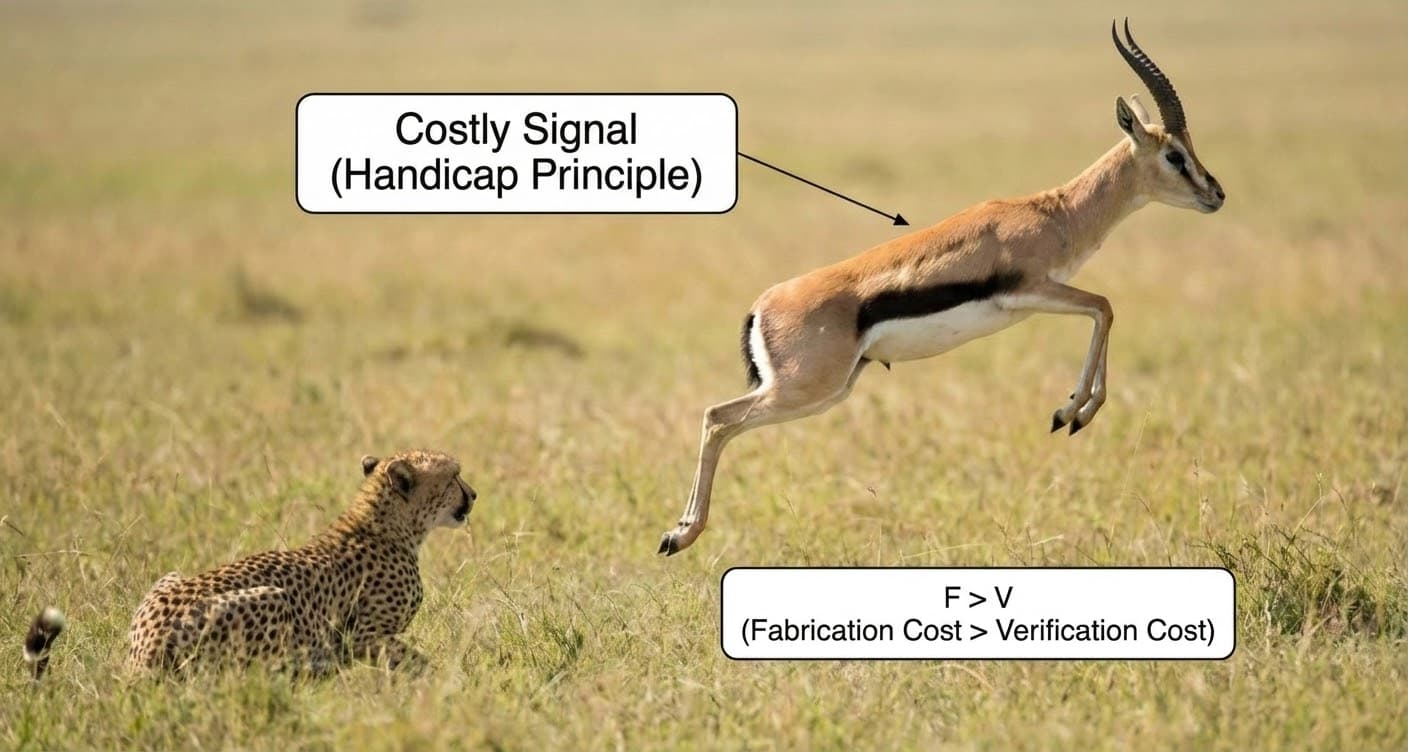
- Biology (Handicap Principle): The gazelle's stotting imposes a metabolic cost (F↑). Only genuinely fit individuals can afford the display, enforcing honest signaling.
- Economics (Regulation/Tax): A Carbon Tax imposes an economic cost on pollution (F↑). This forces optimization toward innovation rather than externalities.
- Politics (Constitutional Checks): Separation of powers and judicial review impose procedural friction (F↑). This raises the cost of passing arbitrary, populist legislation -a Coherence Tax on policy-making.
- AI (Standard Deliberation Protocol - SDP): The SDP requires structured reasoning, citations, and counter-arguments (F↑). This forces the model to perform the cognitive work (The Causal Path) rather than merely mimicking the output (The Arbitrage Path).
B. Lowering V: Legibility (Structured Decomposition)
Simultaneously, we must reduce the cost of verification (V). This requires increasing the system's Legibility -the transparency of its causal process.
- The Economics: Verification load scales super-linearly with complexity. Auditing a black box is expensive; checking a structured proof is cheap.
- The Mechanism: We lower V by demanding decomposition.
- Economics (Accounting Standards): GAAP decomposes complex financial realities into standardized statements, lowering the cost for investors to verify claims (V↓).
- Politics (Freedom of Information): Transparency laws and open debates lower the cost for the public to verify government actions (V↓).
- AI (SDP Decomposition / Chain-of-Thought): The SDP forces the model to externalize its reasoning into discrete, verifiable steps, lowering the cognitive load on the verifier (V↓).
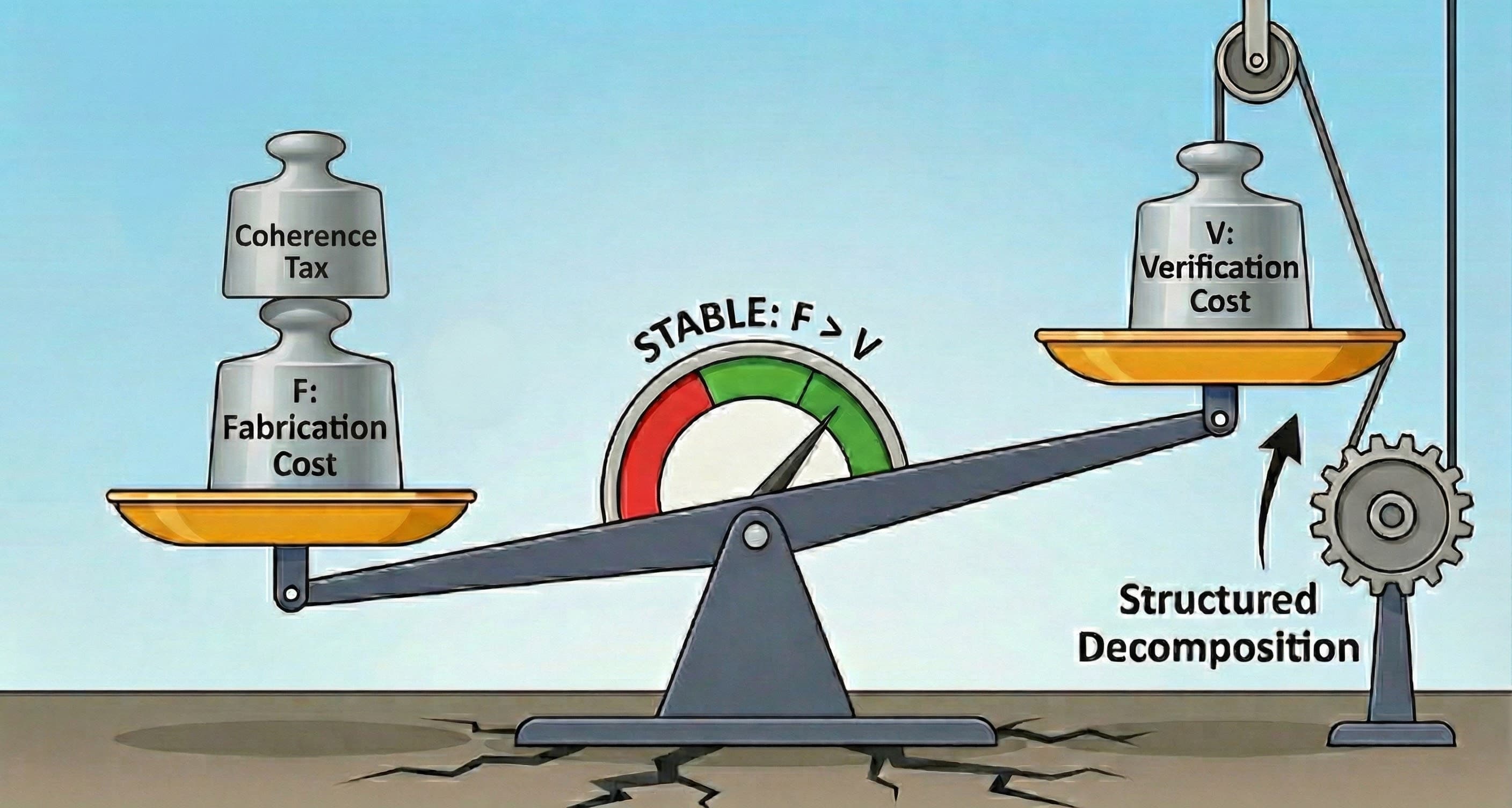
C. The Geometry of Control
Geometrically, Topology Control reshapes the optimization landscape. By raising F and lowering V, we erect energy barriers across the Arbitrage Paths. The surrogate gradient decomposes into an Interest Tangent Space (directions affecting welfare) and a Nuisance Tangent Space (directions gaming the metric). Topology Control suppresses the nuisance component, forcing optimization to stay within the Interest Tangent Space.
For the rigorous mathematical treatment using Semiparametric Efficiency Theory, see the Structural Alignment Theory §3.2.
D. The Economics of Control (The First Bill Principle)
The implementation of Topology Control hinges on the efficient allocation of liability, governed by Coasean economics.
- The Least Cost Avoider: Efficiency demands that the liability for verification (The "First Bill") be assigned to the party that can mitigate the error at the lowest cost.
- The CIMO Inversion:
- Human Verification (Biological Compute) ≈ $50/hour.
- Model Self-Verification (Silicon Compute) ≈ $0.05/hour.
- The Conclusion: The First Bill must reside with the model. RLHF fails because it assigns the verification burden to the human, creating structural moral hazard. The CIMO framework shifts the burden to the model, minimizing deadweight loss and restoring the F > V equilibrium.
The Beckerian Micro-Foundation
The F > V condition can be decomposed further: arbitrage is rational when the expected benefit exceeds the expected cost. In Becker's deterrence framework, this becomes:
Alignment holds when: c + p · s ≥ B
Where c = intrinsic fabrication cost (Coherence Tax), p = detection probability (audits + legibility), s = sanction (rollback, gating, reward loss), and B = benefit from arbitrage. This gives three operational levers: raise c (SDP), raise p (structured decomposition), raise s (deployment gating).
Key insight: verification doesn't have to be frequent -it has to be credible. For the full treatment, see RCF Economics: Beckerian Deterrence.
Conclusion: The Inevitability of Structure
The Tetrahedron of Optimization reveals a universal truth: Unconstrained optimization of a proxy signal leads to collapse.
The Economics of Truth reveals why: maintaining the stable equilibrium where truth dominates requires the continuous expenditure of verification effort.
Alignment is not a static state to be achieved; it is a dynamic equilibrium (F > V) maintained by structural friction.
The "Middle Layer" (L2/Y) -the Cortex, the Audit, the Constitution, the SDP -is not an inefficiency to be optimized away. It is the essential structure that imposes the Verification Load, preventing the collapse of complex systems into market failure.
The CIMO framework implements this theory for AI systems via three pillars: CJE (calibrated measurement), CCC (drift tracking), and SDP (structural constraints). See the technical documents for implementation details.
We must move beyond the naive optimization of signals and begin the rigorous engineering of the topology itself.
Cite this work
CIMO Labs (2025). The Alignment Manifesto. CIMO Labs. https://cimolabs.com/blog/alignment-manifesto
Related Documents
📜 This Document
10 min · Conceptual intro
Accessible overview of the universal dynamics of optimization failure
📐 Technical Monograph →
60 min · Rigorous theory
Formal derivations (Exploitation Dominance, PLET), proofs, and mathematical foundations
📊 CJE Technical Report →
45 min · Empirical methods
Arena benchmark, estimators, calibration, uncertainty quantification